Data Transmission Formats
You have the option to select which data transmission format you want to use. By default all data is transfered in ASCII format. Some commands support binary data transmission (eihter 64-bit or 32-bit format). The data transfer format can be set with :FORMat[:DATA].
The commands that support NON-ASCII data transmission are the following:
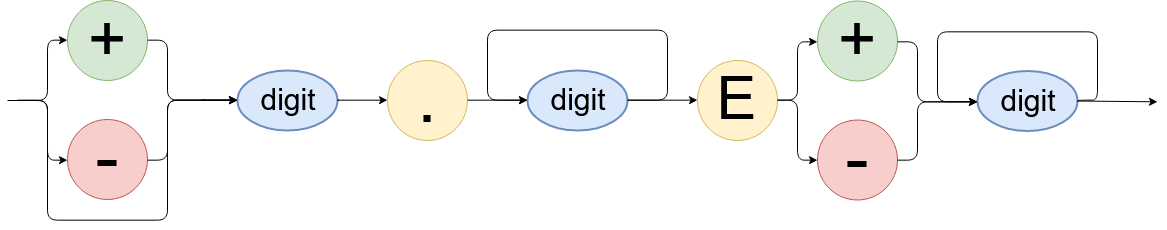
ASCII Transmission
The ASCII Data Transmission format can be selected by calling (:FORM:DATA ASC), but is selected by default.
The figure below shows the ASCII format of decimal values. The value representation is as follows:
- At least 1 digit before the decimal point
- At least 1 digit after the decimal point, up to 10 digits if they are not equal zero
- At least 2 digits for the exponent
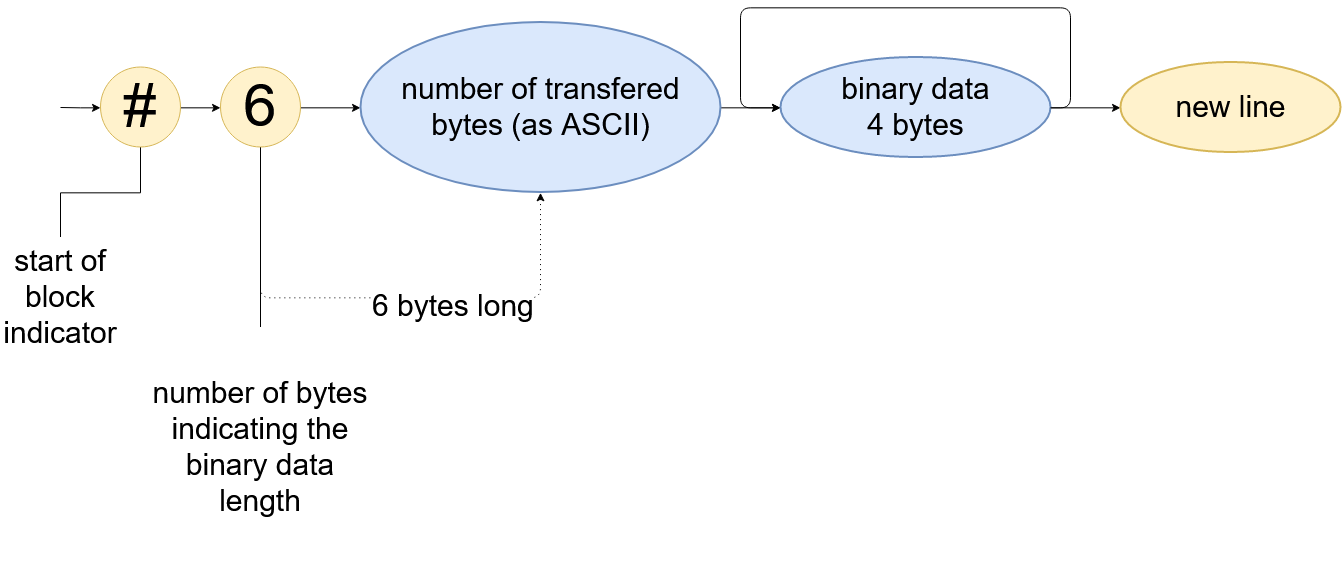
Binary Transmission - 32 Bit
The Binary Data Transmission format (64 bit) can be selected by calling (:FORM:DATA REAL32).
The figure below shows the composition of the Binary Data transfer format (32 bit). It consists of a header and data part. The data is split into sign, exponent and fraction (IEEE standard).
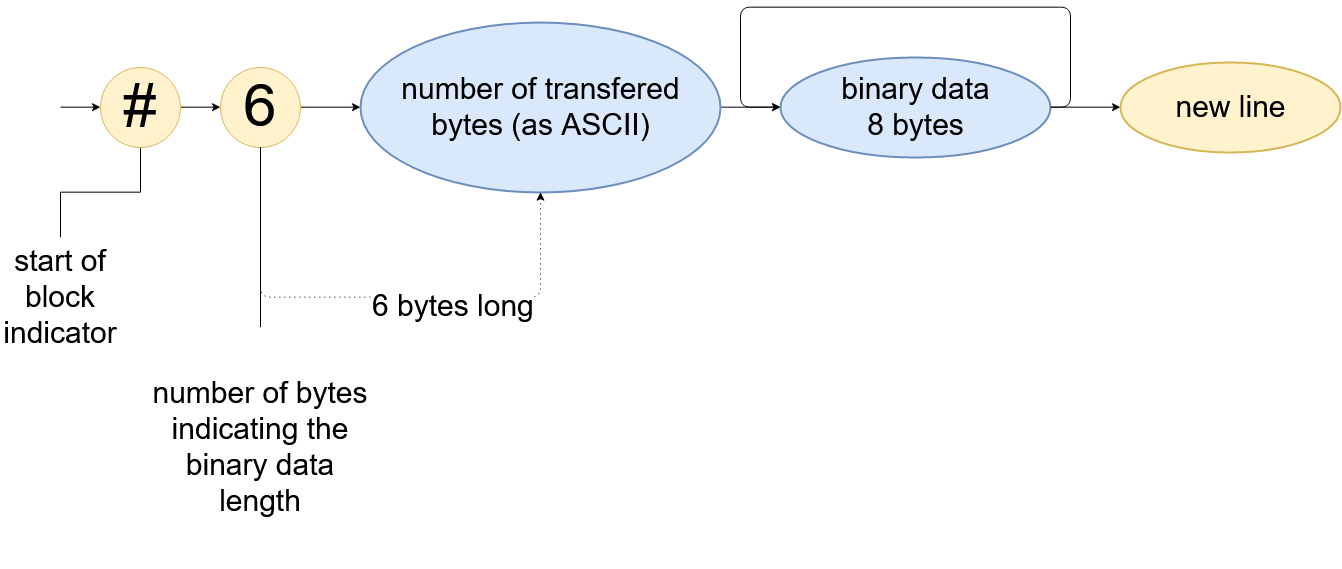
Binary Transmission - 64 Bit
The Binary Data Transmission format (64 bit) can be selected by calling (:FORM:DATA REAL).
The figure below shows the composition of the Binary Data transfer format (64 bit). It consists of a header and data part. The data is split into sign, exponent and fraction (IEEE standard).