Trigger System
Overview
The trigger system is used to enable and initiate measurements.
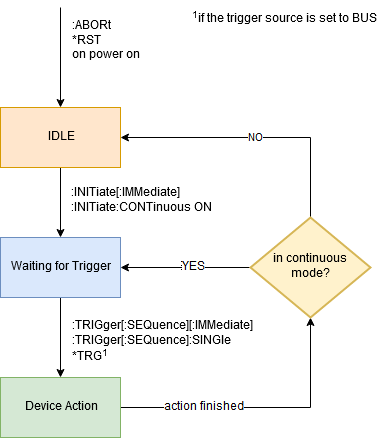
Trigger States
The trigger has three possible states:
- Idle
- Waiting for Trigger
- Action
Idle
After Power ON, :ABORt or *RST the trigger is in the IDLE state. In the IDLE state no trigger signals are accepted and no measurement can be started. To leave the IDLE state, the trigger must be initiated. This can either be done by calling :INITiate[:IMMediate] (the trigger is initiated once) or by setting the trigger into the Continuous Mode (the trigger remains in the initiated mode after a measurement has finished). This can be done with the command INITiate:CONTinuous ON. Then the trigger state switches to Waiting for Trigger.
Waiting for Trigger
The device is waiting for an incoming trigger. If a trigger is recognized, a measurement is started (the trigger state moves to Action). This can be achieved either by supplying an external trigger signal to the device and trigger it that way or by sending one of the following commands:
The device behaves slightly differently depending on the selected trigger command.
| Command | accepted trigger source | awaitable with *OPC? |
|---|---|---|
*TRG |
BUS |
no |
:TRIGger[:SEQuence]:SINGle |
BUS | INTERNAL | EXTERNAL |
yes |
:TRIGger[:SEQuence][:IMMediate] |
BUS | INTERNAL | EXTERNAL |
no |
Action
While in the Action state, the device is performing the selected measurements. When the measurements are completed, the devices behavior depends on whether the trigger is in continuous mode or not (changeable with the INITiate:CONTinuous command). If the device is in the continuous mode, it immediately switches back to the Waiting for Trigger state, otherwise the device returns back to the Idle state.
Trigger Sources
The trigger source specifies which sources the trigger system recognizes as a valid trigger source. It can be set with [TRIGger[:SEQuence]:SOURce]. Possible options are:
| Trigger | Description |
|---|---|
| Bus Trigger | Generates a trigger when the SCPI/IEEE command *TRG is executed. |
| Internal Trigger (to be implemented) | Uses the internal trigger to generate continuous triggers automatically. |
Note
For a continuous measurement the Internal Trigger must be selected and the Continuous Initiation Mode must be enabled. With the internal trigger mode selected the device triggers itself automatically and with the continuous mode enabled the trigger state continuously switches between Action and Waiting for Trigger which results in a continuous measurement.
Commands
A summary of all commands related to the trigger system can be found in the following table.
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
*TRG |
IEEE trigger command; generates a trigger if and only if the source is set to BUS |
:INITiate:CONTinuous {ON\|OFF\|1\|0} |
enables or disables the triggers continuous initiation mode |
:INITiate[:IMMediate] |
changes the trigger state from Idle to Waiting for Trigger |
:TRIGger[:SEQuence]:SINGle |
Generates a single trigger signal and can thereforebe awaited |
:TRIGger[:SEQuence][:IMMediate] |
Generates a trigger signal but cannot be awaited |
:TRIGger[:SEQuence]:SOURce {BUS\|INTernal} |
selects the trigger bus |